In this tutorial, we'll learn how to set up a FastAPI app with a NoSQL database.
We explore how to build a FastAPI application with a NoSQL database, specifically MongoDB, to store and manage data. This guide covers the essential steps for integrating MongoDB with FastAPI, including setting up the database in Docker, defining models, handling data operations, and implementing CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) functionality.
FastAPI is a modern, high-performance web framework for Python, built on standard Python type hints. It's designed to help developers build APIs quickly with automatic validation and interactive documentation. When combined with a NoSQL database, FastAPI offers a robust stack for scalable and flexible web applications.
Prerequisites
- Python Installed: Ensure Python 3.7+ is installed.
- Database Setup: We’ll use MongoDB. Install it locally or use a cloud provider like MongoDB Atlas.
- Environment Setup: Use a virtual environment to manage dependencies.
- Docker must be installed on your system.
Set Up a FastAPI App with a NoSQL Database
Step 1: Create Virtual Environment and Install Required Libraries
First create a project directory and change the current working directory:
mkdir fastapi-nosql && cd fastapi-nosql
Execute following command to create a Python virtual environment:
python3 -m venv venv
Active the virtual environment:
source venv/bin/activate
Install FastAPI, Uvicorn (an ASGI server), and MongoDB’s Python driver.
pip install fastapi uvicorn pymongo motor
- pymongo: Official MongoDB driver.
- motor: An asynchronous MongoDB driver for Python, crucial for integrating with FastAPI’s async capabilities.
Step 2: Project Structure
Run the following commands in your terminal:
mkdir -p app/routes
touch app/main.py app/database.py app/models.py
touch routes/items.py
Organize your project as follows:
fastapi-nosql/
├── app/
│ ├── main.py
│ ├── database.py
│ ├── models.py
│ ├── routes/
│ ├── items.py
Step 3: Deploy MongoDB on Docker
This step is not guiding you to install Docker. The Docker must be installed on your system already.
Create a docker-compose.yml file with the following configuration:
nano docker-compose.yml
Add following content:
services:
mongodb:
image: mongo:latest
container_name: mongodb
restart: always
ports:
- "27017:27017"
environment:
MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME: admin
MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD: securepassword
volumes:
- mongodb_data:/data/db
- mongodb_config:/data/configdb
volumes:
mongodb_data:
driver: local
mongodb_config:
driver: local
Run the following command to start the MongoDB service:
docker-compose up -d
This will pull the MongoDB image, set up the container, and run it in detached mode.
You can verify the container is running with:
docker ps
Step 4: Set Up the Database Connection
In a database.py file, add following code to handle the MongoDB connection.
from motor.motor_asyncio import AsyncIOMotorClient
MONGO_DETAILS = "mongodb://admin:securepassword@localhost:27017/?authSource=admin"
client = AsyncIOMotorClient(MONGO_DETAILS)
database = client.my_database
items_collection = database.get_collection("items")
- Replace
MONGO_DETAILSwith your MongoDB URI. If using MongoDB Atlas, the URI will include credentials and cluster information. - The
items_collectionwill store documents for our example CRUD application.
Step 5: Define the Data Model
Use Pydantic to create data validation models in models.py.
Open models.py and add following code:
from bson import ObjectId
from pydantic import BaseModel
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: str
price: float
in_stock: bool
class Config:
allow_population_by_field_name = True
arbitrary_types_allowed = True
json_encoders = {ObjectId: str} # Custom encoder for ObjectId
Step 6: Create CRUD Operations
Define database operations in database.py. Open database.py and update the following code:
from bson import ObjectId
from .models import Item
# Convert MongoDB document to dictionary
def item_helper(item) -> dict:
return {
"id": str(item["_id"]),
"name": item.get("name", ""), # Default to an empty string if the field is missing
"description": item.get("description", ""),
"price": item.get("price", 0.0), # Default to 0.0 for missing price
"in_stock": bool(item.get("in_stock", False)), # Default to False for missing in_stock
}
async def retrieve_items():
items = []
async for item in items_collection.find():
items.append(item_helper(item))
return items
async def add_item(item_data: dict) -> dict:
item = await items_collection.insert_one(item_data)
new_item = await items_collection.find_one({"_id": item.inserted_id})
return item_helper(new_item)
async def retrieve_item(id: str) -> dict:
item = await items_collection.find_one({"_id": ObjectId(id)})
if item:
return item_helper(item)
async def update_item(id: str, data: dict):
if len(data) < 1:
return False
item = await items_collection.find_one({"_id": ObjectId(id)})
if item:
updated_item = await items_collection.update_one(
{"_id": ObjectId(id)}, {"$set": data}
)
if updated_item:
return True
return False
async def delete_item(id: str):
item = await items_collection.find_one({"_id": ObjectId(id)})
if item:
await items_collection.delete_one({"_id": ObjectId(id)})
return True
Step 7: Build API Endpoints
In routes/items.py, add following code:
from fastapi import APIRouter, HTTPException
from ..models import Item
from ..database import (
retrieve_items,
add_item,
retrieve_item,
update_item,
delete_item,
)
router = APIRouter()
@router.get("/")
async def get_items():
items = await retrieve_items()
return items
@router.post("/")
async def create_item(item: Item):
new_item = await add_item(item.dict())
return new_item
@router.get("/{id}")
async def get_single_item(id: str):
item = await retrieve_item(id)
if not item:
raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="Item not found")
return item
@router.put("/{id}")
async def update_item_data(id: str, item: Item):
updated = await update_item(id, item.dict(exclude_unset=True))
if not updated:
raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="Item not found")
return {"message": "Item updated successfully"}
@router.delete("/{id}")
async def delete_item_data(id: str):
deleted = await delete_item(id)
if not deleted:
raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="Item not found")
return {"message": "Item deleted successfully"}
Step 8: Initialize the Application
In main.py, set up the FastAPI application.
from fastapi import FastAPI
from app.routes.items import router as ItemRouter
app = FastAPI()
app.include_router(ItemRouter, prefix="/items", tags=["Items"])
@app.get("/")
def root():
return {"message": "Welcome to the FastAPI NoSQL application"}
Step 9: Run the Application
Run the app using Uvicorn.
uvicorn app.main:app --reload
Visit http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs for interactive API documentation provided by FastAPI.
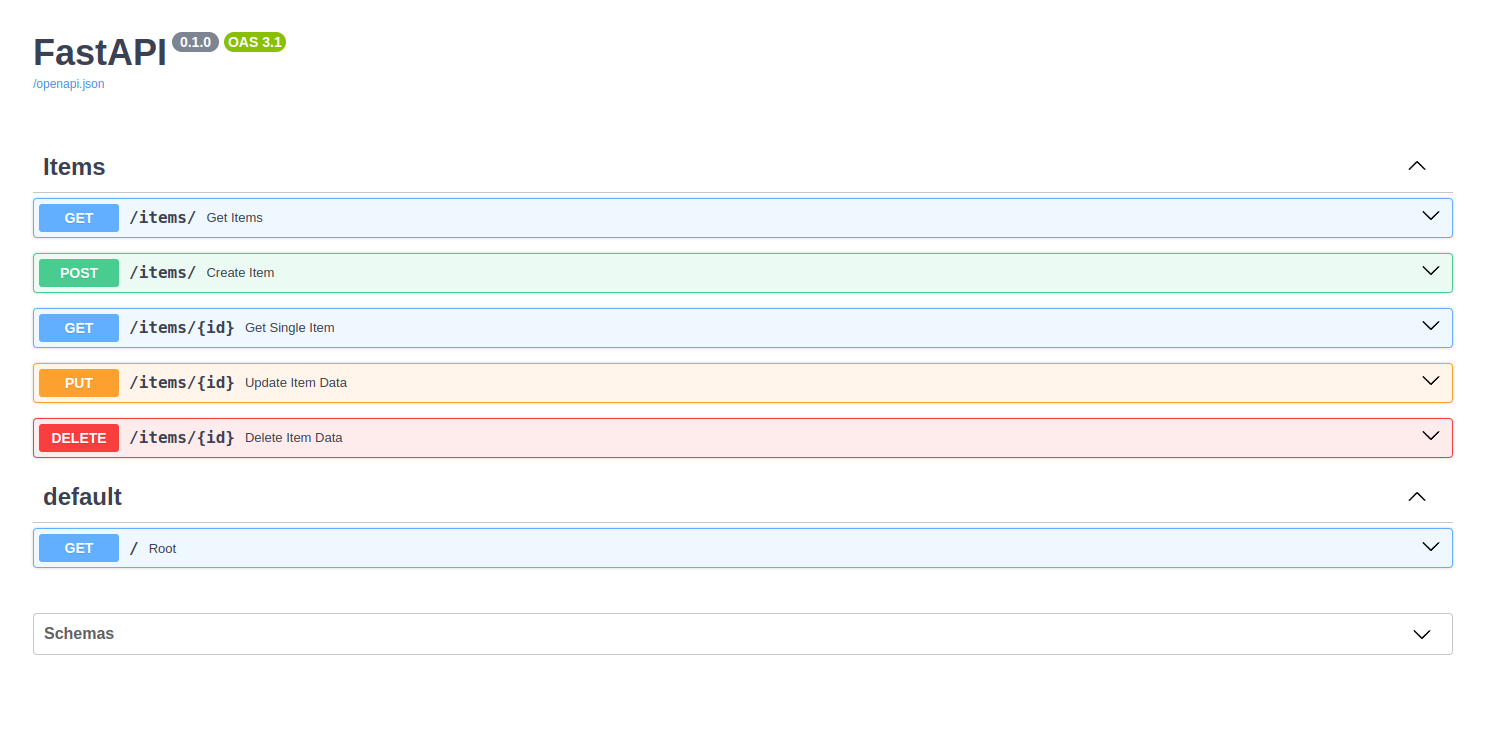
Step 10: Test the API
Get All Items: GET /items
Create an Item: POST /items with a JSON body:
{
"name": "Laptop",
"description": "A powerful laptop",
"price": 1200.99,
"in_stock": true
}
Get Single Item: GET /items/{id}
Update an Item: PUT /items/{id}
Delete an Item: DELETE /items/{id}
Step 11: Deploy Your Application
To deploy, you can use services like Docker, Heroku, or AWS Lambda. For Docker:
Create a Dockerfile.
nano Dockerfile
Add following content:
FROM python:3.9
WORKDIR /app
COPY ./app /app
RUN pip install fastapi uvicorn pymongo motor
CMD ["uvicorn", "app.main:app", "--host", "0.0.0.0", "--port", "80"]
Build and run the Docker container.
docker build -t fastapi-nosql .
docker run -d -p 80:80 fastapi-nosql
In this tutorial, we'll learnt how to set up a FastAPI app with a NoSQL database. We’ve built a FastAPI application integrated with a NoSQL database. This stack is scalable, modern, and efficient, making it an excellent choice for many applications.
Checkout our dedicated servers India, Instant KVM VPS, and Web Hosting India

